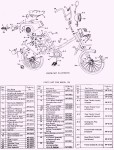
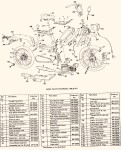
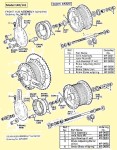
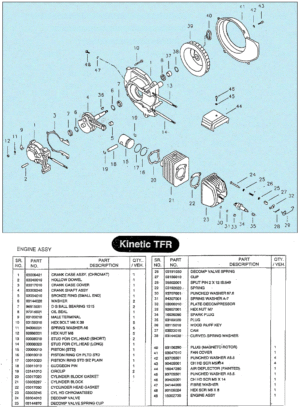
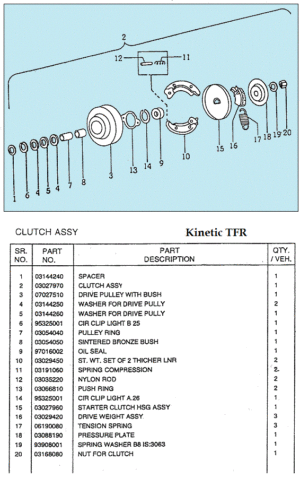
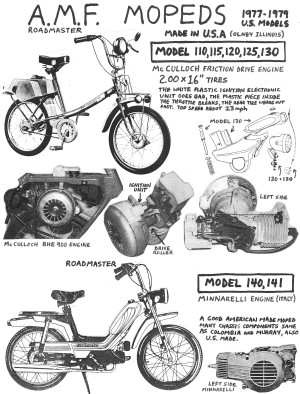
AMF made in USA by AMF McCulloch or Minarelli engine
AMF made in USA by AMF McCulloch or Minarelli engine
Here is an excerpt from Wikipedia: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/American_Machine_and_Foundry Aug 2014
American Machine and Foundry was once one of the largest recreational equipment companies in the United States. The company was founded in 1900 by Rufus L. Patterson, inventor of the first automated cigarette manufacturing machine. Originally incorporated in New Jersey but operating in Brooklyn, the company began by manufacturing cigarette, baking, and stitching machines. AMF moved into the bowling business after World War II, when AMF automated bowling equipment and bowling centers became profitable business ventures. Bicycle production was added in 1950. The company was once a major diversified manufacturer of everything from tennis racquets to bowling equipment. Until the mid-1980s, AMF’s range of consumer goods included powered model airplanes, snow skis, lawn and garden equipment, Ben Hogan golf clubs, Voit inflatable balls, exercycles and exercise equipment, Hatteras yachts, Alcort sailboats, Nimble bicycles, motorized bicycles, mopeds, and SCUBA gear. At one time, AMF owned Harley Davidson motorcycles. Aging production facilities and increasing quality control problems in some product lines caused sales declines in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The company’s vast diversified output proved difficult to efficiently manage, and after suffering a series of losses, the company began to sell off most of its manufacturing operations.
AMF Roadmaster Bicycles In 1950, after purchasing the Roadmaster line of children’s and youth bicycles from the Cleveland Welding Company, American Machine and Foundry entered the bicycle manufacturing business with its newly formed AMF Wheel Goods Division. In 1953, after a prolonged labor strike, AMF moved bicycle manufacturing from a UAW-organized plant in Cleveland, Ohio to a new facility in Little Rock, Arkansas. The new plant was heavily automated and featured more than a mile of part conveyor belts in six separate systems, including an electrostatic induction painting operation.
Taking advantage of the increase in its target markets in the aftermath of the baby boom, AMF was able to diversify its product line, adding exercise equipment under the brand name Vitamaster in 1950. As demand for bicycles continued to expand, the company needed a new manufacturing facility to keep up with demand. In 1962, the company moved its operations to Olney, Illinois, where it built a new factory on a 122-acre site that would remain the company’s principal bicycle manufacturing location into the 1990s.
After two decades of consistent growth, the AMF Wheel Goods Division stalled under the long-distance management of a parent company bogged down in layers of corporate management and marginally profitable product lines. Manufacturing quality as well as the technical standard of the Roadmaster bicycle line – once the pride of the company – had fallen to an all-time low. Bicycles made at the Olney plant were manufactured so poorly that some Midwestern bike shops refused to repair them, claiming that the bikes would not stay fixed no matter how much labor and effort was put into them. The division’s problems with quality and outside competition were neatly summed up in a 1979 American film, Breaking Away, in which identical secondhand AMF Roadmaster track bicycles were used by competitors in the Little 500 bicycle race. Despite this product placement, the film’s protagonist expressed a decided preference for his lightweight Italian Masi road racing bike, deriding the elderly Roadmaster as a ‘piece of junk’.
In 1997, the Roadmaster bicycle division was sold to the Brunswick Corporation. However, it had already become evident that production of low-cost, mass-market bicycles in the US was not viable in the face of foreign competition, and in 1999, all U.S. production of Roadmaster bicycles ceased. Brunswick sold its bicycle division and the Roadmaster brand to Pacific Cycle, which began distributing a new Roadmaster line of bicycles imported from Taiwan and the People’s Republic of China. Pacific Cycle still uses the Olney facility for corporate offices and as a product inventory and distribution center.
 AMF Bowling products In 1943, Rufus Patterson’s son, Morehead Patterson, took over AMF. After WWII ended, Patterson determined that the company had to ‘grow or die’. Searching for new products, he encountered a prototype of an automatic bowling-pin setter. To get the cash to develop the invention, Patterson swapped AMF stock to acquire eight small companies with fast-selling products. After incorporating key features developed by Leslie L. LeVeque, the AMF Pinspotter, perfected and put on the market in 1951, helped to turn bowling into the most popular US participative, competitive sport.
AMF Bowling products In 1943, Rufus Patterson’s son, Morehead Patterson, took over AMF. After WWII ended, Patterson determined that the company had to ‘grow or die’. Searching for new products, he encountered a prototype of an automatic bowling-pin setter. To get the cash to develop the invention, Patterson swapped AMF stock to acquire eight small companies with fast-selling products. After incorporating key features developed by Leslie L. LeVeque, the AMF Pinspotter, perfected and put on the market in 1951, helped to turn bowling into the most popular US participative, competitive sport.
AMF High-tech products In 1949 American Machine and Foundry developed the pretzel bender, a new automatic crispy styled baked pretzel-twisting machine that rolled and tied them at the rate of 50 a minute, more than twice as fast as skilled hand twisters could make them, and conveyed them through the baking and salting process. To expand its line of recreational equipment, AMF bought W. J. Voit Rubber Corp. (tread rubber, scuba gear), Ben Hogan Co. (golfing equipment), and Wen-Mac Corp. (engine-powered toy airplanes). By 1961, AMF controlled and operated 42 plants and 19 research facilities scattered across 17 countries, producing everything from remote-controlled toy airplanes to ICBM launching systems. AMF was the builder of the launching silos for the Titan and Atlas ICBMs, and also developed the rail-car launching system for the solid-fueled Minuteman ICBM. In the late 1950s and early 1960s the company ran neck-and-neck with General Dynamics in the construction of nuclear power reactors. AMF sold Pakistan and Iran their first nuclear reactors. Peter Karter was among the young engineers working on the reactors AMF built in Pakistan and Iran under the Atoms for Peace program. In 1960 the company moved its headquarters from 249 Madison Avenue, Manhattan, to suburban Westbury, New York. In the early 1960s, American Machine and Foundry partnered with the French company SAFEGE to design, construct and market a monorail for American cities. The AMF Monorail was exhibited at the 1964 New York World’s Fair where it traversed a continuous elevated loop around the Amusement section of the Fair. It was displayed as a practical form of future transportation.
 AMF Roadmaster Mopeds
AMF Roadmaster Mopeds
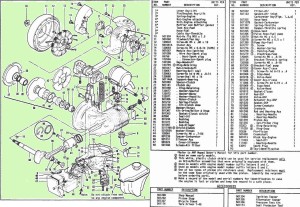
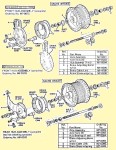
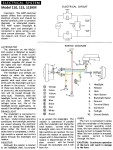
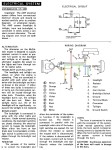
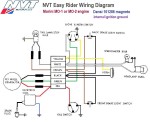
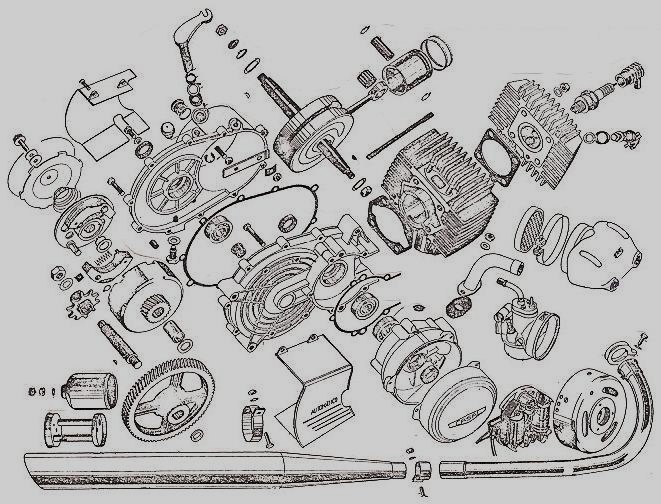
 After building elevated monorails and nuclear missile launchers, you would think making a moped would be relatively easy. But AMF was late in the game, and had to rush through the design. In 1977, Europe had 30 years experience making mopeds. There was a huge demand for mopeds in the US, more than Europe and Asia could satisfy. Other American bicycle makers Murray and Colombia were beginning to make mopeds with European engines and components. AMF had plenty of bicycle making expertise, but not small engines. So AMF teamed up with McCulloch in 1977 to make this BHE900 rear friction-drive one-speed automatic 49cc two-stroke moped engine. McCulloch already made high quality, compact, light weight two-stroke engines for the hand-held-power-equipment industry – chain saws, blowers, trimmers, etc. But the AMF moped engine was a brand new design. The presence or absence of a pull starter supports that. Gardening equipment engines adapted to bicycles have rope-pull starters, while “pure” bicycle engines can only be pedal started. In about a year it went from just a sparkle in an engineer’s eye, to 1000’s of units rolling off the assembly line by the end of 1978.
After building elevated monorails and nuclear missile launchers, you would think making a moped would be relatively easy. But AMF was late in the game, and had to rush through the design. In 1977, Europe had 30 years experience making mopeds. There was a huge demand for mopeds in the US, more than Europe and Asia could satisfy. Other American bicycle makers Murray and Colombia were beginning to make mopeds with European engines and components. AMF had plenty of bicycle making expertise, but not small engines. So AMF teamed up with McCulloch in 1977 to make this BHE900 rear friction-drive one-speed automatic 49cc two-stroke moped engine. McCulloch already made high quality, compact, light weight two-stroke engines for the hand-held-power-equipment industry – chain saws, blowers, trimmers, etc. But the AMF moped engine was a brand new design. The presence or absence of a pull starter supports that. Gardening equipment engines adapted to bicycles have rope-pull starters, while “pure” bicycle engines can only be pedal started. In about a year it went from just a sparkle in an engineer’s eye, to 1000’s of units rolling off the assembly line by the end of 1978.
McCulloch BHE900 Moped Engine
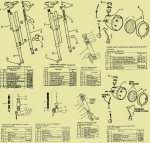
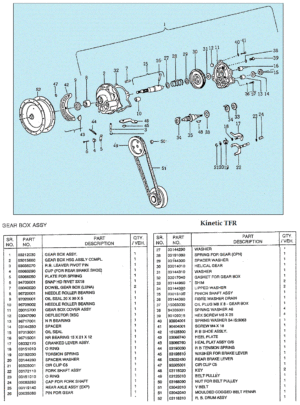
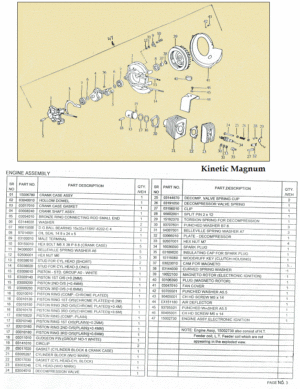
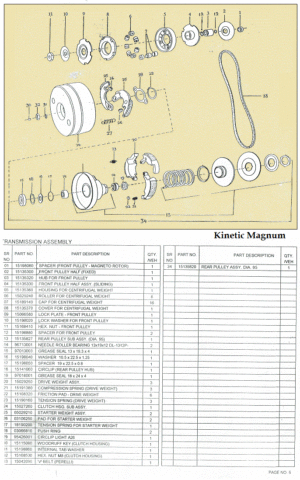
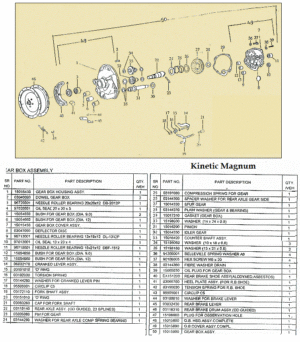
Myrons Mopeds does not have any AMF/McCulloch parts, except for a few random bits, and things used on other mopeds, like piston rings, bearings, gas cap, fuel hose, spark plug, crank nut, etc. The above parts list says there are different reed valves for the D and E engine versions, but gives the same part numbers for replacement parts. The reed valve and carburetor are the only things that are different on those more powerful engine versions. When the details of this become known, you will read about it here.
model # carb fuel pump power speed AMF Models 400612B T.K. separate 1.0 hp 20 mph 110, 115, 120 400612C Keihin separate 1.0 hp 20 mph 110, 115, 120 400612D Zama built-in 1.0 hp 20 mph 115, 120, 125 400612E Zama built-in 1.0 hp 20 mph 115, 120, 125AMF Roadmaster (110)

1978 AMF Roadmaster
Model 110, 2.0 – 16″ tires
orange w/orange fenders
20 mph, 1.0 hp, 68 lbs
Grimeca drum brakes,
Sun Metal rims

1980 AMF Roadmaster
Model 110 orange/orange
Messenger black saddle
20 mph, 1.0 hp, 68 lbs
170 mpg, list $379

1979 AMF Roadmaster,
engine cover removed, Zama carb with built-in diaphragm fuel pump. Carlisle flat-top tires
In 1980 this was the lowest priced new moped, at $379, the highest was $1069, for the Puch Magnum MkII.
AMF Roadmaster (115)

1978 AMF Roadmaster
Model 115
red with orange fenders
20 mph, 1.0 hp, 68 lbs
Peterson head, tail lights
Carlisle flat-top tires

1979 AMF Roadmaster
with engine uncovered. It’s a friction drive, on flat-top tire, with an automatic centrifugal clutch
AMF Roadmaster XL (120)

1978-79 Roadmaster XL
Model 120 (20mph)
front suspension fork
0.38 gallon gas tank
updated electrical wiring

1979 Roadmaster XL
Model 120 orange/white
Stewart-Warner speedo
AMF front suspension
updated electrical wiring
Peterson gold bullet HL
AMF Roadmaster XL (125)

1979-80 Roadmaster XL
Model 125 (20mph?)
front suspension, speedo
0.38 gallon gas tank
updated electrical wiring

1979 Roadmaster XL
Model 125 wheat/gold
Peterson gold bullet HL
F susp, Sun Metal rims
Grimeca drum brakes
Messinger gold saddle
Stewart-Warner speedo

1979 Roadmaster XL
Model 125 wheat/gold
engine part # 400612D The C or D suffix means it has a Zama carb with built-in fuel pump, and a better reed valve.

1980 Roadmaster XL
Model 125 wheat/gold
This one has no engine, mountain bike bars, and bicycle lights. Many road masters have become sidewalk masters.

1980 Roadmaster XL
Model 125 ? (20mph?)
white/wheat/gold fenders
0.83 gal tank, no speedo
gold Peterson headlight
normal rear lift lever

AMF Roadmaster mopeds 1981 flyer page 3-4
left, 130, wheat/gold, 25 mph, 1.5 hp, 88 lbs, F susp, speedo, handlebar mount lift lever
mid, 120, colors redwood/wheat, 20 mph, 1.0 hp, 72 lbs, front suspension, speedometer
right, 110, orange/orange, 20 mph, 1.0 hp, 68 lbs, no front suspension, no speedometer
AMF Roadmaster XL (130)

1980 Roadmaster XL
Model 130 (25mph)
white/wheat/gold fenders
0.83 gallon tank, speedo
engine lift lever on bars
gold Peterson bullet HL

1980 Roadmaster XL
Model 130 (25mph)
white/wheat/gold fenders
0.83 gal, speedometer
engine lift lever on bars
gold Peterson bullet HL

AMF Roadmaster mopeds 1981 flyer page 1-2, Minarelli V1 engine model 140/141
Left, dark w/light tank and fenders. Right, light w/dark tank and fenders. (not made?)
Only “dark w/light tank and fenders” was made, with solo or long seat, 25 or 30mph.
AMF Roadmaster (140 or 141)

1980 AMF Golden Arrow,
Model 140 (30 mph) with black fan shroud that is normally light grey, same rims and tires as 110.
0.83 gallon gas tank

1980 AMF Golden Arrow
Model 140 (30 mph)
Minarelli V1 engine
Messenger black saddle
Grimeca hubs and brakes
extra left starter lever

1980 AMF Roadmaster
Model 141 (25 mph)
wt 100 lb, Minarelli V1
0.83 gallon gas tank
Carlisle 2.25 – 16 tires

1982 AMF Roadmaster
Model 141 (25 mph)
Minarelli V1 engine
Dellorto SHA 14/12 carb
Peterson black bullet HL
Huret speedometer

1983 AMF Roadmaster
Model 140 (30 mph)
metallic grey with silver
Minarelli V1 engine
extra left start lever
AMF Model 140 and 141 are identical, except for the Minarelli engine. The long seat option must have began in late 1981 or 1982, because only a solo seat AMF 140 is listed in the 1981 Buyers Guide. After 1980, the 110, 120, 130 rear engine models were apparently not made, because all of the 1981 and later AMF’s pictured on the internet are the Model 140/141 Minarelli-engine kind. The Minarelli AMF lasted until 1983-84 when sales were way down.
The End of AMF Mopeds
![]()
 By the mid-1980’s, falling gas prices, new state moped laws, and the craze for Japanese scooters, ended the demand for mopeds in the US. Sometime around 1984, AMF sold their remaining moped and parts inventory to “E-Z Rider”, also known as K.E.Z. Industries Inc, 430 E 16th St, Paterson NJ 07514. KEZ sold AMF Roadmaster parts to moped dealers across the US, starting in 1985. They only sold the frame parts, not the McCulloch or Minarelli engine parts. By the late 1980’s there were not many moped dealers left in business.
By the mid-1980’s, falling gas prices, new state moped laws, and the craze for Japanese scooters, ended the demand for mopeds in the US. Sometime around 1984, AMF sold their remaining moped and parts inventory to “E-Z Rider”, also known as K.E.Z. Industries Inc, 430 E 16th St, Paterson NJ 07514. KEZ sold AMF Roadmaster parts to moped dealers across the US, starting in 1985. They only sold the frame parts, not the McCulloch or Minarelli engine parts. By the late 1980’s there were not many moped dealers left in business.
There seems to be a connection between two E-Z Riders. In 1979-1980 there was an American made moped called E-Z Rider, made by Dialex Industries, Inc. 123 S. Newman St. Hakensack, New Jersey 07671. Like AMF, it was sold by Montgomery Wards department stores. Like AMF, it had a Minarelli V1 engine with a mix of American and Italian components. The Dialex E-Z Rider had a plastic gas tank with this logo embossed on it. Notice how both E-Z Rider logos are spelled the same and both companies are from New Jersey. Most likely Dialex Industries either became, or was bought by, KEZ Industries.
Myrons Mopeds does not have any actual AMF moped parts for sale, except for the many things that are the same as other mopeds, and maybe some random bits and pieces. This collection of information is here for several reasons: 1) artwork and history for your enjoyment, 2) to help find what parts go where or what might be the same, 3) to refer to particular parts by name, number, illustration, or photo.
Here are links to Project Moped Manual for AMF Moped Manuals. This is a 1979 AMF Roadmaster Owners Manual. The rear McCulloch engine is separate, 1978 McCulloch BHE900 Engine Owners Manual. These download in a minute or two, in PDF format.
AMF Tires
For the friction drive models 110/115/120/125/130 the original Carlisle (made in USA) tires are labeled “2 – 16 moped”. But 2.0 – 16 size tires are difficult or impossible to get. Most mopeds with 16″ rims have 2.25 -16, or 1/4 inch wider. The front Carlisle 2 -16 with zig-zag tread is 2.0 inch wide, but the rear tire with the smooth flat top is actually 2.20 inch wide. In front there is plenty of room for a 2.25 -16 but in the rear there is barely room for the original tire that is 2.2 inch wide. A 2.25-16 is also 2.20 (or 2.25) inch wide. It might not rub if the axle is spaced to center it, but otherwise it would rub.
Considering that, it is better to use actual 2.00 – 16 tires, or the equivalent 20 x 2.125 bicycle tires. There are 20 x 2.125 bicycle tires with a smooth top, but rounded. Those would be best. Worst would be a knobby style. The smooth top lasts longer.