Yamaha Wiring: Yamaha made the QT50 Yamahopper moped (actually “no-ped” or “mokick”) from 1979 to about 1983. There are 2 or 3 wiring and electrical equipment versions. more later…
Wards Riverside Wiring: Mongomery Wards in the late 1960’s sold a full line of motorcycles and mopeds made in Italy by Benelli (and also early 1960’s mopeds made in France by Motobecane). This is the 50cc sport bike model FFA-14003, a 4-speed foot shift manual clutch motorcycle.
Even back then, they used the ignition source coil ground to operate the brake light. Ground the green wire first to get spark.
Here “universal” means applies to most but not all.
Universal Points-Magneto Ignition Wiring, External or Internal Ground
Universal Wiring Harness, brake light wires can be norm open in parallel or normally closed in series
Universal Wiring Actual, this is for sale in electrical/wiring/
Testi Wiring: Testi makes Gitane, Red Foxi, and other makes with Minarelli V1 engines. See Minarelli Wiring.=
Tomos Wiring: Here is a complete, detailed, and accurate set of wiring diagrams. These took 200 hours, over a 3-month period, to gather, interpret, colorize, and edit for clarity. Many of the originals were terribly inadequate, although functionally correct.

Tomos A3 wires needed to have spark
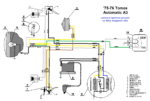
Tomos (US models)
’75-76 Automatic
Ducati 31.17.30 magneto
3-wire, 6V 40w lights
external ignition ground
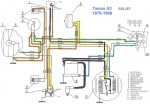
Tomos (US models)
’76-79 A3SP, A3GM, A3SL
Ducati 31.17.30 magneto
3-wire, 6V 40w lights
external ignition ground

Tomos (US models)
’79-82 A3 Bullet
Ducati 31.17.30 6V 40w
’83-86 A3 Bullett
Ducati 31.17.30 6V 40w
or ZEM 31.17.30 6V 40w
external ignition ground
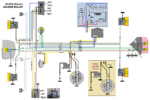
Tomos (US models)
’79-85 Silver Bullet
’85-86 Golden Bullet
Ducati 31.17.30 6V 40w
or ZEM 31.17.30 6V 40w
or CEV 6951 6V 28/10w
external ignition ground
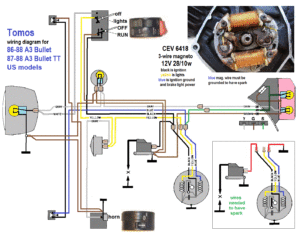
Tomos (US models)
’86-88 A3 Bullet
’87-88 A3 Bullet TT
CEV 6418 3-wire 12V 28/10w
external ignition ground
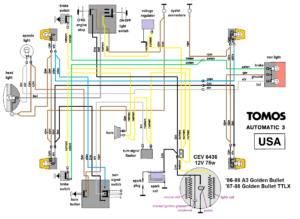
Tomos (US models)
‘86-88 A3 Golden Bullet
’87-88 Golden Bullet TTLX
CEV 6436 2-wire 12V 75w
internal ignition ground
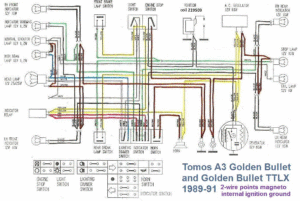
Tomos (US models)
’89-91 A3 Golden Bullet TTLX
square headlight
Iskra 1215 2-wire 12V 50w
internal ignition ground
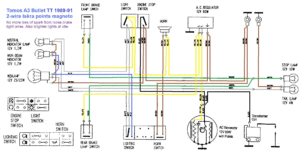
Tomos (US models)
’89-91 A3 Bullet TT
square headlight
Iskra 1215 2-wire 12V 50w
internal ignition ground
After 1991 all Tomos magnetos had an internal ignition ground.
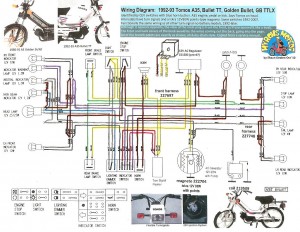
Tomos (US models)
’91-93 A35 Bullet, Bullet TT
’92-93 A35 Golden Bullet, TTLX
Iskra 1217 2-wire 12V 80w
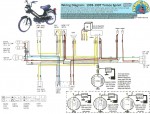
Tomos (US models)
’93-94 Sprint (A35)
IDM 6436 or IDM 6411
’94-95 Sprint, Sprint TT
IDM 6436 or Iskra 1217
or AET 11.160.053
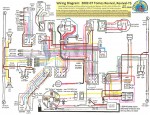
Tomos (US models)
’02-03 Revival (A35)
AET 11.170.017 12V 80w
’04-07 Revival TS (A55)
AET 11.170.026 12V 80w
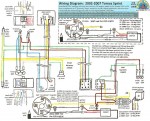
Tomos (US models)
’02-06 Sprint (A35)
AET 11.170.001 12V 80w
’07-08 Sprint (A55)
AET 11.170.027 12V 80w
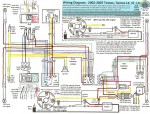
Tomos (US models)
’02-06 Tomos, LX (A35)
’05-06 ST (A35)
AET 11.170.001 12V 80w
’07-08 ST, LX (A55)
AET 11.170.027 12V 80w
Trac Wiring: Trac mopeds were made in Korea by Dailim (DMC). Early Tracs were a mix of European and Asian components and designs.
Later Tracs were all Asian, with wire colors same as Honda.
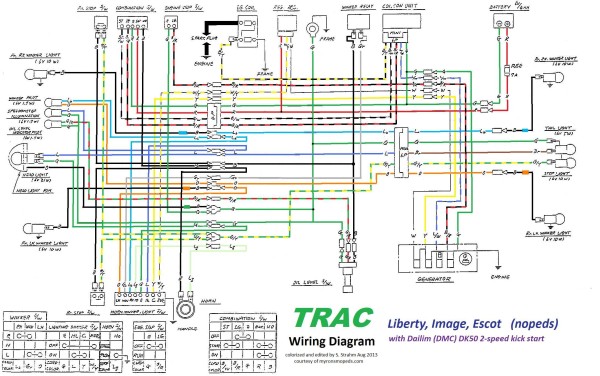
Trac 1986-89 with turn signals, Liberty, Image, Escot
Daelim DK50 2-speed, CDI 5-wire magneto, internal ignition ground
![]() The DMC DP50 engine (one-speed with pedals) used on Olympic, Clipper, Hawk and DK50 engine (two-speed kickstart) used on Liberty, Image, Escot, engines both had a 5-wire CDI magneto. White = battery charging, yellow = head light, blue/white = ignition pulse, black/red = ignition power, green = ground.
The DMC DP50 engine (one-speed with pedals) used on Olympic, Clipper, Hawk and DK50 engine (two-speed kickstart) used on Liberty, Image, Escot, engines both had a 5-wire CDI magneto. White = battery charging, yellow = head light, blue/white = ignition pulse, black/red = ignition power, green = ground.
There are two CDI units that look the same. Here the key switch is bypassed by joining the two black/red male bullets. The engine stop button (black/white) is also disconnected. This apparatus has good spark, when the wheel is spun counterclockwise by hand. Note that the coil is grounded.
The DMC DH100 (4-speed 97cc 4-stroke overhead cam motorcycle) had a 3-wire magneto/generator down in the oil bath, with external points and condenser up on the overhead cam. Very much the same as a Honda 90, except the Trac had a ignition source coil in the generator, while most versions of Honda 90’s did not . A 1986 Trac DH100 would run with a dead or missing battery, but a 1971 Honda Trail 90 would not. These similar small motorcycles are examples of the difference between a battery ignition and a magneto ignition system.
Sachs (Hercules) Wiring: Sachs mopeds, made by Nürnberger Hercules Werke GMBH, should not be confused with mopeds that have Sachs engines, like General, Grycner, Clinton, Colombia, AMS, Foxi, Sparta, Flying  Dutchman, Eagle, and many others. Most of the “true” Sachs mopeds can be identified by the Hercules “H” logo stamped into the headlight mounts. Sachs early models, roughly 1976-1978, had an internal ignition ground. Those never lost spark because of bad brake light wires. Sachs later models, roughly 1978-1981, had an external ground. Those had a secret ignition ground resistor hidden inside the CEV 2-bulb tail light. If that went bad, the ignition would not have spark when either brake was applied (or all the time, if the brake light switch wires were loose). In that case attach the ignition ground wire, that comes out of the engine, to ground. It’s blue/black for Bosch magnetos, and black for Motoplat magnetos. That will restore the spark, but disable the brake light, for emergency use or troubleshooting.
Dutchman, Eagle, and many others. Most of the “true” Sachs mopeds can be identified by the Hercules “H” logo stamped into the headlight mounts. Sachs early models, roughly 1976-1978, had an internal ignition ground. Those never lost spark because of bad brake light wires. Sachs later models, roughly 1978-1981, had an external ground. Those had a secret ignition ground resistor hidden inside the CEV 2-bulb tail light. If that went bad, the ignition would not have spark when either brake was applied (or all the time, if the brake light switch wires were loose). In that case attach the ignition ground wire, that comes out of the engine, to ground. It’s blue/black for Bosch magnetos, and black for Motoplat magnetos. That will restore the spark, but disable the brake light, for emergency use or troubleshooting.
Sachs (Hercules) Wiring for Hercules-made mopeds with Sachs 505 engines (pedals inside engine):
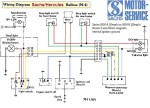
Sachs Balboa M-4 (USA)
Sachs 505/1A or 1B eng
Bosch 90mm 5-wire mag
internal ignition ground
ULO 2-bulb tail light

Sachs 1980 Suburban
wires inside head light.
Behold, the “mystery”
diode that powers the
horn from the ignition.

Sachs Suburban 1978-on
shows magneto wires plug
505/1D with Bosch 3-wire
external ignition ground
CEV 2-bulb tail lite w/res
Sachs (Hercules) Wiring for Hercules-made mopeds with Sachs 504 engines (pedals outside engine):

Sachs Westlake P-1 (USA)
made by Nürnberger
Hercules Werke GMBH
Sachs 504/1A or 1B eng
Bosch 4-wire 80mm mag
internal ignition ground

Sachs 1978 Westlake P-1
504/1A w/Bosch 4-wire
internal ignition ground
identified by black coil
ULO 2-bulb tail lite
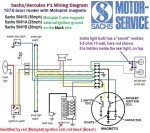
Sachs/Hercules 1978-on
Westlake,Sundancer (P-1)
Sachs 504/1D,1A,1B
Motoplat 3-wire magneto
external ignition ground

Sachs 1978 Westlake P-1
504/1D Motoplat 3-wire
external ignition ground
identified by red ign coil
CEV 2-bulb tail lite w/res
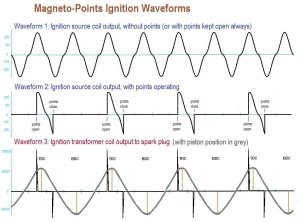
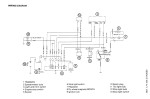
Ignition Waveforms: Interrupted AC
Curve 2 shows how the points interrupt the source,
and cause the unused negative triangular sections.
On a Hercules, they get less when the horn is used.
On all other bikes those minus voltages are unused.
“Mystery” Diode: All Hercules-made mopeds borrow electric power from the ignition wire (not the ignition ground) to power the horn. Normally this would kill the spark. But the wise Germans found some unused power. It’s a little hard to understand, without lots of pictures and hand waving. The flywheel has four bar magnets aligned N to N and S to S, so there are two Norths and two Souths per revolution. The current generated reverses direction every 90 degrees. The points open (the spark moment) near one of the magnetic maximums, say North. About 45 degrees later, the field is zero, and heading South. The points stay open for about 20 or 40 more degrees. That’s when there’s a short period of available reverse current/power. (When the points finally close, a secondary weaker spark occurs, with reverse polarity, but has no effect on the already burned gas.) The diode allows that reverse current to flow to the horn instead of to the spark coil, so no secondary reverse spark is produced at the spark plug when the horn is on. The diode one-way-gate stops the forward current from flowing out to the horn, so the main spark is not affected. The main spark only needs the forward current and not the reverse.
Always disconnect the power diode, aka “Mystery Diode”, and the engine stop switch, when troubleshooting for no spark, on a Hercules-made moped. It’s either inside the head light, or down near the engine. It is for making the horn not dim the headlight.
Sachs 504 Engine with Motoplat (made in Spain) 80mm magneto/flywheels are used on some Hercules, Sparta, and KTM mopeds. They are gold colored, and have the number 9600089. The wires are yellow = lights, blue = ignition, black = ignition ground. Their points have a built-in red wire. Condenser is CEV-compatible.

Sachs ’78 P-1 with 504/1D
Motoplat 3-wire magneto
top: ignition – blue, black
bottom: lites coil – yellow
Motoplat 80mm flywheels used on 1976-86 Derbi mopeds have the number 9600099. Those wires are red = lights, green = ignition, blue = ignition ground. Their points are different, and also have no built-in wire. Condenser is CEV-compatible.
Sears Free Spirit Wiring: The Free Spirit moped, made by Kromag, has the same wiring and electrical equipment as 1977-78 Puch Maxi (6-wire). In fact, the whole bike is Puch, but it doesn’t say “Puch” anywhere on it. All of the brand markings have been removed, to make it seem like Sears made it. Like all the Bosch 6-wire magneto Puch wirings, the blue/black wire that powers the horn is an external ignition ground for the source coil. Unplug the horn wires and loosen the light/horn switch clamp from the handlebar, and a Free Spirit will loose spark and not run. Also, like 78-later Puch, the horn button does the opposite of all other horn buttons in the world. It is normally closed, and when you push, it is momentarily open. If you replace it with any other horn button, the horn would be on all the time, and go off when you push the button. To eliminate the chance of loosing spark due to bad horn wires, simply gound the blue/black magneto wire at the terminal strip above the engine, by moving it over to the brown wire that goes to ground.
Solex Wiring: The 1970’s and earlier Solex 3800 had only one wire outside of the engine, going to the tail light. Instead of wires, the head light and switch had direct contacts. The ignition spark coil was internal, with the spark plug wire coming out of the magneto.
Soni Wiring: This 1980’s India remake of a 1970’s Italian made Vespa/Piaggio moped, has functionally the same wiring, pretty much, as Vespa did. Unlike the Kinetic, a 1990’s India made Vespa remake, that has a CDI ignition, the Soni has points, and an external ignition ground magneto that powers the brake light, like Vespa/Piaggio. When we say “ground the pink wire to get spark if the brake light filament burns out”, in India they say “earth when stop light is fused”. It looks like it has an emergency wire that would allow it to run if it lost spark from a blown brake light bulb or loose wire.
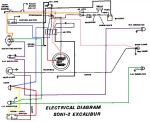
Soni 2 Excalibur Wiring
turn signal model
India made Vespa Ciao
3-wire points magneto
external ignition ground
Sparta Wiring: Sparta had two 80mm magneto versions for the Sachs 504 engine, Bosch 4-wire and Motoplat 3-wire. The wires on the bike are the same, except Motoplat version has an external ignition ground, a tail light secret resistor, brake switch type NC not NO, and the brake switches wired in series, not parallel. The Motoplat version needs the brake light wires and correct bulb to have spark.
One way to tell which (brake light) wiring and magneto version a Sparta has, from a distance, is by the color of the ignition coil and plug wire. Motoplat is red, while Bosch is black. It’s the same situation as Hercules/Sachs wiring. Spartas with red coils have normally closed (white or brass tip) brake light switches in series, and a secret brake light resistor-diode circuit board inside the tail light. Spartas with black coils have normally open (black tip) brake light switches in parallel, and no brake light resistor inside the tail light.
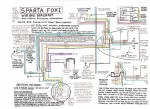
Sparta Foxi, early F.D.
with many notes added
ULO 2-bulb early taillight
Bosch 4-wire magneto
internal ignition ground
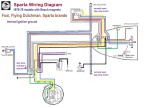
Sparta (with Bosch)
’76-78 Foxi, F.D, Sparta
ULO 2-bulb early taillight
Bosch 4-wire magneto
internal ignition ground
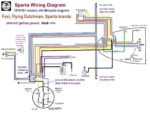
Sparta (with Motoplat)
’78-81 Dutchman, Sparta
ULO 2-bulb taillight w/res
Motoplat 3-wire 9800089
external ignition ground
Suzuki Wiring: The early 1980’s Suzuki FZ50 (3.00 x 12″ tires) and FA50 (2.25 x 14″ tires) have pretty much the same engine, controls, wiring, and electrical equipment.
Rizzato Wiring: Italian made Rizzato has it’s own engine, with either a CEV 6952 or a Dansi 3-wire magneto. Rizzato Califfo uses the same wiring and wire colors as Italian-made mopeds with Minarelli engines. Red is ignition, black is lights, and blue (for CEV) or green (for Dansi) is an external ignition ground, powering the brake light. Unpluging the brake light wires on a Rizzato will make it stop running. When it has no spark, always ground the blue wire first. Outside wiring disconnected is often the cause.
Pacer Wiring: Pacer is an Italian moped with either a Morini MO1, MO2, or M1 engine. Early models with frame number 15499 and below, all have the Dansi 101286 3-wire 3-coil magneto, with the ignition source coil grounded internally. Later models with frame number 15500 and above can have either 101286 or the Dansi 101765 3-wire 2-coil magneto. The only way to tell is by the number stamped on the flywheel. The brake light switches, wiring harness, and tail light are different for each magneto type. See also Morini Wiring.
Peugeot Wiring: Peugeot was one of 3 or 4 moped makers that made their own magneto. The French maker chose to be different and make their flywheel have puller threads M20x1.0, instead of the Germans M22x1.5 or Italians M19x1.0. Pre-1980 Peugeots have an external ignition ground running the brake light. Remove the tail light assembly or unplug the wires and it won’t run. Ground the black wire under the engine by attaching it somewhere to ground (such as the tail of the decomp cable wire), to get spark, when there is no spark. 1980 and later Peugeots do not have that problem, because they have an internal ignition ground. Their ignition does not rely on any of the lights.
Peugeot Ignition Upgrade: Way back in the mid 1980’s, Peugeot 103 mopeds, 1976-1979 began to burn up condensers and points rapidly. Some of the coils would send voltage spikes. In the late 1980’s the supply of coils and stators had pretty much been used up. By 1990, even brand new Peugeot coils would not work good for long. They were going bad just sitting on the shelf. Out of desperation Shaun found a substitute inner source coil, from a Puch. It fits the Peugeot coil bolts, if they are bent in a little. A Puch outer coil (transformer) was added onto the right frame near the carburetor. ’78-79 and some ’77 103’s already have the external coil mount. 1977-earlier has to be welded on. There is a whole chapter about that here.
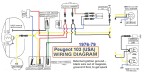
Peugeot 103 1976-79
103 LS, 103 LVS, 103 SP
3-wire + spark magneto
internal transformer with
external ignition ground
These 1980 and later Peugeot models already have the upgraded ignition, with external transformer coil.
Piaggio Wiring: Vespa is one brand of the parent company Piaggio. For 1970’s Vespa mopeds, there many wiring diagrams with photos and service info, located in a separate Service section, under Vespa Electrical https://www.myronsmopeds.com/category/vespa-electrical/
Puch Wiring: All 1978-1986 Puch mopeds, USA models, have a 6-wire Bosch magneto, with points, and with an external ignition ground that powers the horn. Unplugging one of the horn wires, then pressing the horn button stops the engine. In addition to that, loosen the horn/light switch clamp from the handlebar, and a brand new Puch will not run, because of disconnected horn wires. Really! Puch is the only maker that chose to meet the USA standards that way. Almost everyone else chose to power the brake light with the ignition ground. Maybe the others figured if you’re already using the brakes and your engine dies, it’s not as bad.
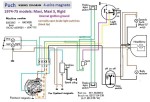
Puch 1974-75 (4-wire)
Maxi, Maxi-S, Rigid (GN)
Maxi 8353263-8421028
Rigid 6539521-6547172
4-wire Bosch magneto
1-speed 0212 124 038
internal ignition ground
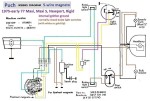
Puch 1976-77 (5-wire)
Maxi-N, Maxi-S, Nostalgic
Maxi 8421029-8709891
Rigid 6547173-6830115
5-wire Bosch magneto
1-speed 0212 124 042
internal ignition ground

Puch 1976-77 (5-wire)
Maxi-N, Maxi-S, Nostalgic
actual wiring laid out
ULO 2-bulb tail light
Merit chrome switches
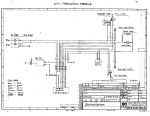
Puch Schaltplan Jun-77
The original 6-wire plans,
for US models, where the
ignition powers the horn.
external ignition ground
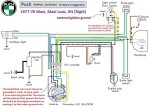
Puch 1977-78 (6-wire)
Maxi, Maxi Luxe, Rigid
Maxi 8709892-???????
Rigid 6830116-???????
6-wire Bosch magneto
1-speed 0212 124 043
external ignition ground
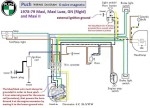
Puch 1978-79 (6-wire)
Maxi, Maxi II, Luxe, Rigid
6-wire Bosch magneto
1-speed 0212 124 043
2-speed 0212 124 044
external ignition ground
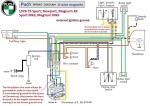
Puch 1978-79 (6-wire)
Sport, Newport, Magnum
Sport MkII, Magnum MkII
1-speed 0212 124 043
2-speed 0212 124 044
external ignition ground

Puch 1978-79 (6-wire)
Sport, Newport, Magnum
Sport MkII, Magnum MkII
w/square black switches
CEV 2-bulb tail light
external ignition ground
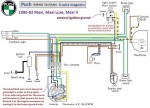
Puch 1980-82 (6-wire)
Maxi, Maxi II, Maxi Luxe
1-speed 0215 254 658
2-speed 0215 254 674
external ignition ground
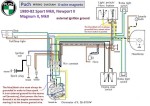
Puch 1980-82 (6-wire)
Sport MkII, Newport II,
Magnum II, MkII
2-speed 0215 254 674
external ignition ground

Puch 1980-82 (6-wire)
Sport MkII, Newport II
Magnum II, MkII
w/square black switches
external ignition ground
Puch 1980-82 (6-wire)
Magnum MkII, Limited Ed
with ignition key switch
2-speed 0215 254 674
external ignition ground
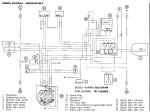
Puch 1983-84 (6-wire)
Maxi, Dart with
6VAC voltage regulator
1-speed 0215 254 658
external ignition ground
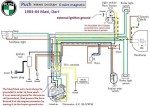
Puch 1983-84 (6-wire)
Maxi, Dart with
6VAC voltage regulator
original b & w diagram
external ignition ground

Puch 1984-86 (6-wire)
Maxi Sport LS, MS LS II
Cobra, Cobra II, ’85 Maxi
w/square black switches
external ignition ground
Puch Re-makes: After the last Austrian made Puch in 1986, three companies have reproduced the 1980’s Puch mopeds. Piaggio (Italy, early 90’s), Hero (India, late 90’s), and Manet (Hungary, late 90’s). While the most of engine is the same, the electrical equipment and wiring is different, more modern. All 1990’s and later mopeds have CDI ignitions with an internal ignition ground. Thanks to the advent of electronic solid state voltage regulation in the mid 1980’s, allowing stronger magneto/generators (50 or 80 watts instead of 30) without bulb burnout, modern mopeds don’t need to borrow “juice” from the ignition, so their ignition is separate from the lights or horn, and thus way more reliable.
Odyssey Wiring: Odyssey mopeds and engines are made in Germany by Solo. They have German style wiring with separate generator wires for each light. Euro models have a Bosch 0212 005 011 80mm clockwise magneto. USA models have a Bosch 0212 124 039 90mm clockwise magneto. More to follow…
Negrini Wiring: The wiring diagram is not in the owners manual by MMI. See Morini Wiring. What number is on the magneto flywheel determines one of two possible wiring schemes. See Morini Wiring and Dansi Magnetos.
NVT Wiring: NVT (Norton Villiers Triumph) mopeds and motorcycles are made in England. The Easy Rider ER1 and ER2 mopeds all use the Dansi 101286 magneto, according to the owners manual wiring. On that magneto/generator, the lighting coil is split into two concentric coils, one for brake light and horn (black wire), and one for head light, tail light, and speedo light (green wire). The other coil is ignition (red wire), with an internal ground, so it is isolated from the lights.
Manet Wiring: This is a mid to late 1990’s Puch remake, made in Hungary by Manet. It is better known as the “Puch Korado”. Some things, like the engine, are the same as Puch, but the electrical and wiring is all different. Like all the other all-AC modern (1990’s and later) mopeds, the Korado has all the lights on one wire, with a 12VAC shunt-type voltage regulator. Like everything modern, it has a completely separate and independent CDI (capacitor discharge ignition) system that in no way depends on the lights. The CDI has no pulser coil.
Manet/Korado also made the mid-to-late-1990’s Jawa remake. The wiring for that not currently available, but is expected to be close to this wiring and electrical equipment.
Minarelli Wiring: Most Italian mopeds, US models, that have Minarelli engines have this same wiring, functionally. Many have the same exact colors as well. There are at least 21 names: Aspes, Baretta, Bianchi, Cimatti, Concord, Fantic, Gadabout, Gitane, Intramotor, Lem, Maico, Motomarina, Motron, Pryer, Red Foxi, Safari, Silver Foxi, Snark, Testi, Yankee Peddler, and others. They all have the Minarelli V1 or V1L engine with CEV 6932 3-wire magneto with external ignition ground (blue wire) powering the brake light. Ground the blue wire first if there is no spark.
Morini Wiring: Franco Morini moped engines can have two possible Dansi magnetos. Which one it has is determined by a number stamped on the flywheel. Some Italian mopeds, US models, that have Morini engines have this same exact wiring. This “universal” wiring can be configured for either NC-in-series (for Dansi 101765 or 101732), or NO-in-parallel (for Dansi 101286 magneto) brake light switches. Most others wirings are functionally the same as one of these two versions. There are dozens of brand names: Arciero, Benvenuti, Bianchi, Colt, Cosmo, F. Morini (no relation to Franco Morini), Intramotor, Italjet, Italvelo, Italtelai, Lem, Malaguti, Motomarina, Motobecane, Negrini, Pacer, Snark, Velomec, West Wind, and others. Morini is only the engine name.
Dansi magneto 101286 3-wire 2-coil
has normally open brake light switches in parallel
and an internal ignition ground.
Dansi magnetos 101765 and 101732 3-wire 3-coil
have normally closed brake light switches in series
and an external ignition ground that powers the brake light.
Motobecane Wiring: Two versions for USA model mopeds.
Early “6 volt” version: Before Jan 1978, Motobecane mopeds had a 2-coil Novi magneto, with an external ignition ground. The ignition assisted in keeping the lights bright, in a complex way.
Later “12 volt” version: After Jan 1978, Motobecane mopeds had a 3-coil Novi magneto, with an internal ignition ground. However, the ignition coil still needs at least one of the two neighboring lighting coils to be active. Amazingly, the lights not working can make it loose spark, even though they are not connected. It has to be from the magnetic field. The wiring is also complex.
Euro version: They were much simpler. No brake light and less watts.
Moto Guzzi Wiring: There are two kinds of Moto Guzzi Robin. They have the same name but different frames and wiring. Moto Guzzi made a stamped sheet-metal frame model, called Chiù in Europe, and Robin in the US. They also sold a Robin with a mono-tube frame made by Seimm. Both kinds had the 1970’s Motobi (Benelli) moped engine, with a Dansi 3-wire magneto.
Moto Guzzi Robin (mono-tube) The mono-tube Moto Guzzi Robin is identical to a Benelli G2. The Dansi 3-wire magneto had an external ignition ground on the green wire. It must always be connected to ground to have spark.
Moto Guzzi Robin (sheet frame) The sheet frame Moto Guzzi Robin is the US version of Chiù. The Dansi 101441 3-wire magneto had an internal ignition ground. It would never loose spark because of loose brake light wires, but the lights are not as bright.
Motron Wiring: Functionally the same as the “Minarelli Wiring”. 1978-79 had the CEV clamp-on plastic slide switches. 1980-81 had the CEV “diamond” switches integrated (fitted into) the Domino controls.
Murray Wiring: Same as Puch Series B. Bosch 6-wire with external ignition ground powering the horn. Ignition, brake light, tail light, and head light all have separate source coils (armatures). Ground the blue/black wire first if there is no spark.